Content
Businesses around the world might differ in operating industry, sector, and geographic location. However, almost all businesses are united in the suffering of phishing attacks targeting their users.
14 Sep 2022

Introduction
Businesses around the world might differ in operating industry, sector, and geographic location. However, almost all businesses are united in the suffering of phishing attacks targeting their users. Such attacks could be easy to spot by tech-savvy users. Nevertheless, a sophisticated phishing attack could even trick trained users, posing a critical threat and forming a great chance for threat actors to achieve their goals. Moreover, one of the most interesting elements is the variation of the targets, as some users were observed to receive a large volume of phishing emails, while others are receiving a relatively less amount. This advisory aims to uncover the most used techniques by threat actors to obtain the email addresses of the organization’s users to initiate the phishing campaign.
Sources of Email Addresses
Publicly Exposed Accounts
In this case, the threat actors attempt to obtain the email addresses of the users belonging to the targeted entities by searching for any mailboxes associated with the entity's domain in search engines, public resources, and deep web resources such as paste sites. Users in many cases are unintentionally exposing their business emails in LinkedIn or Github accounts as a communication means. However, threat actors will always take advantage of such exposed details to target the users. Additionally, organizations should abstain from publishing content that contains users’ email addresses. The email addresses that can be published are the generic accounts that represent organization departments such as info, HR, marketing, and legal mailboxes.
B2B Directory
A B2B business directory is basically an online directory that is listing businesses around the world, categorizing businesses, and collecting their contact details; aiming to guide users and help them in their search for companies for marketing/business purposes. However, services such RocketReach, Zoominfo, Apollo, Hunter, and SignalHire are truly a goldmine for malicious actors to obtain a user's contact details. These online databases of businesses have their own methodologies for obtaining, verifying, and then selling the employees’ contact details of an entity. B2B directories provide such information for business purposes; hence, most of them also provide a “removal request” feature in their platform so the targeted entity will be allowed to contact them in order to remove their own data from the B2B Directory platform. In the Appendix, we have listed the most common B2B Directory platforms along with their contact details to request the removal of the organization’s details.
Email Syntax Guessing
In this case, the attacker is capable of guessing multiple user mailboxes, either by searching for the email format used by a specific entity or by guessing the generic department's mail lists, such as Public Relations, IT Department, or HR. In this case, the threat actor is not looking for a specific email account; instead, the goal here is to identify the email format being adopted by an organization. Then, the threat actor will work on identifying the employee’s names from public sources such as LinkedIn and map the employee’s name to the organization’s email format. For example, the threat actor was able to identify that the email format followed by XYZ organization is “{First Initial}.{Last Name}@xyz.com”. Then, by exploring the LinkedIn page of XYZ organization, the actor was able to find an employee with the name “John Smith”. Therefore, the threat actor will attempt to target this specific user by sending the phishing email to the mailbox “jsmith@xyz.com” which will likely be a valid email address for the user.
Third-Party Data Breaches
Data breaches are the leakage of an organization's sensitive information, including the Personally Identifiable Information (PII) related to the organization’s users or customers. The breached information is not limited in most cases to email addresses or passwords. Breaches can include the exposure of dates of birth, geographic locations, names, employer name, gender, and phone numbers. Once a third-party entity - such as social media or any service provider - is breached, the malicious actor will tend to sell the data to the public. Such data exposure represents a great source of information for threat actors as for sure some information of the organization's employees will be part of such breaches due to the registration in the breached party. By acquiring the dumps of data breaches and looking for the details associated with the users belonging to the targeted entity, this method can be utilized by the attackers to perform more sophisticated attacks. Users that are using their corporate email accounts for the registration of third-party services are for sure highly vulnerable to this type of information exposure.
Phenomenon: Targeting Personal Inboxes With CxO Name
CTM360 witnessed an increase in a sophisticated attack willing to lure the victims by delivering the phishing email to the victim’s personal inbox. Hence, the victim would be in a tough situation where he might be in a direct encounter with the threat actor; far away from the corporate defenses. The attack scheme is mostly utilizing compromised mailboxes from well-reputed email providers, using a C-level executive name as a sender, and requesting urgent action to be performed from the victim. Such details are actually aligned with the scope of advisory, where the attacker is taking advantage of the exposed details in data breaches, which includes useful information such as email addresses, job titles, employers, names, phone numbers, and social media profiles. Then, the attacker is mapping and correlating these exposed details to the victim profile of the targeted entity and initiates the Phishing attack targeting the victim’s personal mailbox.
Recommendations
In order to protect your organization from email exposure, the following steps are recommended to be taken:
-
Ask your employees to remove their business account details if it was published online.
-
Reach out to the B2B directories listing your users requesting the removal of the accounts.
-
Use generic mailboxes in your online publications such as HR, Marketing, or Legal.
-
Ensure to have a strict policy regarding the registration in online third-party services.
-
Ensure not to use the same email address pattern across the organization. Use different email patterns such as:
- {LastName}@xyz.com
- {First_Initail}{LastName}@xyz.com
- {FirstName}{LastName}@xyz.com
- {LastName}{First_Initial}{Middle_Initial}@xyz.com
Appendix
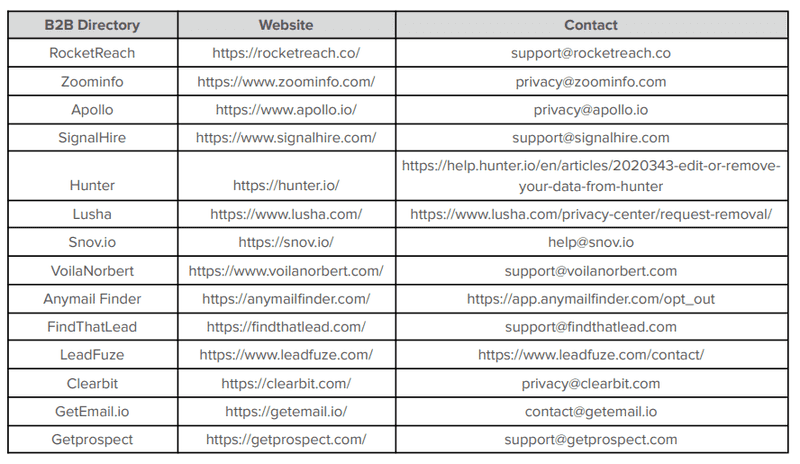
This table contains the most popular B2B directories along with their contact information for removal requests.





